Have you ever noticed how your skin can sometimes act up, just like a moody teenager? One day, you might wake up with a pimple, and the next, you could find your skin feeling itchy or dry. These little skin issues might seem minor, but they can actually be signs of something more significant going on beneath the surface.
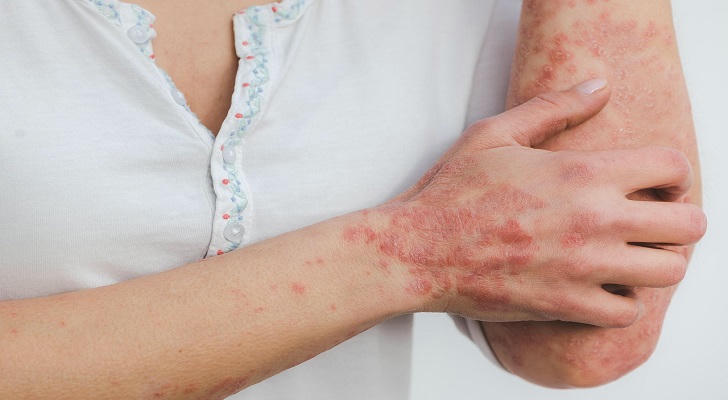
In this blog post, we’re going to explore some of the most common skin problems, from pesky acne to stubborn eczema, and even the more serious conditions like psoriasis and herpes. Don’t worry—we won’t be using complicated medical jargon! Instead, we’ll break things down in a way that’s easy to understand.
By learning about these skin conditions and their causes, you’ll be better equipped to take care of your skin and keep it healthy. So, are you ready to discover some simple tips and tricks to help your skin behave? Let’s dive in!
Common Types of Skin Diseases
1. Acne
- Description: Affects oil glands in the skin, leading to clogged pores and breakouts.
- Causes: Hormonal changes, excess oil production, bacteria, and dead skin cells.
- Prevention: Maintain a regular skincare routine, avoid touching the face, and use non-comedogenic products.
2. Eczema (Atopic Dermatitis)
- Description: A chronic condition characterized by dry, itchy, and inflamed skin.
- Causes: Genetic factors, environmental triggers, and immune system dysfunction.
- Prevention: Moisturize regularly, avoid known irritants, and manage stress levels.
3. Psoriasis
- Description: An autoimmune condition that leads to red, scaly patches on the skin.
- Causes: Genetic predisposition, immune system issues, and environmental triggers.
- Prevention: Avoid triggers such as stress and smoking, and maintain a healthy lifestyle.
4. Herpes
- Description: A viral infection causing painful blisters, typically around the mouth or genitals.
- Causes: Infection with the herpes simplex virus (HSV).
- Prevention: Practice safe sex, avoid sharing personal items, and manage outbreaks with antiviral medications.
5. Hives (Urticaria)
- Description: Raised, itchy welts on the skin, often due to allergic reactions.
- Causes: Allergens, stress, infections, and certain medications.
- Prevention: Identify and avoid triggers, and consider antihistamines for relief.
6. Ringworm (Tinea)
- Description: A fungal infection that causes ring-shaped, red patches on the skin.
- Causes: Fungal spores from contaminated surfaces or direct contact with infected individuals.
- Prevention: Keep skin dry, avoid sharing personal items, and maintain good hygiene.
General Prevention Tips for Skin Health
- Hydration: Drink plenty of water to keep skin hydrated.
- Sun Protection: Use sunscreen to protect against UV damage.
- Healthy Diet: Consume a balanced diet rich in vitamins and antioxidants.
- Regular Check-ups: Visit a dermatologist for skin assessments and early detection of issues.
- Stress Management: Engage in activities that reduce stress, such as exercise and meditation.

Benefits and Risks of Surgical Skin Grafting for Skin Disease Treatment
Benefits:
-
Restoration of Skin Integrity: Surgical skin grafting can effectively restore the integrity of the skin in areas affected by severe skin diseases, burns, or trauma. This can improve the overall appearance and function of the skin.
-
Improved Healing: Grafting can promote faster healing in damaged areas by providing a new layer of skin that can help protect underlying tissues and reduce the risk of infection.
-
Pain Relief: For patients suffering from chronic skin conditions or wounds, skin grafting can alleviate pain associated with open wounds or damaged skin.
-
Enhanced Functionality: In cases where skin diseases affect mobility (such as in joint areas), grafting can improve skin flexibility and functionality, allowing for better movement.
-
Psychological Benefits: Restoring the appearance of the skin can have significant psychological benefits for patients, improving self-esteem and quality of life.
Risks:
-
Infection: As with any surgical procedure, there is a risk of infection at the graft site or in the donor area. Proper care and hygiene are essential to minimize this risk.
-
Rejection of the Graft: The body may reject the graft, especially if the graft is taken from a different individual (allograft). This can lead to complications and may require additional procedures.
-
Scarring: Surgical grafting can result in scarring at both the donor and recipient sites. The extent of scarring can vary based on individual healing processes and the size of the graft.
-
Limited Success: Not all grafts will take successfully. Factors such as blood supply, the condition of the surrounding skin, and the patient's overall health can affect the success rate.
-
Pain and Discomfort: Patients may experience pain and discomfort during the recovery period, which can vary depending on the extent of the surgery and individual pain tolerance.
-
Cost and Accessibility: Surgical skin grafting can be expensive and may not be covered by insurance in all cases, making it less accessible for some patients.
In summary, while surgical skin grafting can offer significant benefits for treating skin diseases, it is essential to weigh these against the potential risks. Consulting with a qualified healthcare professional can help determine the best course of action based on individual circumstances.

Frequently Asked Questions (FAQs)
-
What are the most common skin diseases?
- The most common skin diseases include acne, eczema, psoriasis, herpes, hives, and ringworm.
-
What causes acne, and how can I prevent it?
- Acne is caused by hormonal changes, excess oil production, bacteria, and clogged pores. To prevent it, maintain a regular skincare routine, avoid touching your face, and use non-comedogenic products.
-
Is eczema contagious?
- No, eczema is not contagious. It is a chronic condition often triggered by genetic factors, environmental irritants, and allergies.
-
How can I tell if I have psoriasis?
- Psoriasis typically presents as red, scaly patches on the skin, often accompanied by itching or discomfort. If you suspect you have psoriasis, it’s best to consult a dermatologist for a proper diagnosis.
-
What are the triggers for hives?
- Hives can be triggered by allergens, stress, infections, certain medications, and even temperature changes. Identifying and avoiding these triggers can help manage outbreaks.
-
Can herpes be cured?
- Currently, there is no cure for herpes. However, antiviral medications can help manage outbreaks and reduce the risk of transmission.
-
How can I protect my skin from sun damage?
- To protect your skin from sun damage, use a broad-spectrum sunscreen with at least SPF 30, wear protective clothing, and seek shade during peak sun hours.
-
When should I see a dermatologist?
- You should see a dermatologist if you notice persistent skin issues, sudden changes in your skin, or if over-the-counter treatments are not effective. Early intervention can help prevent more serious conditions.

Conclusion
Understanding the various types of skin diseases, their causes, and preventive measures can significantly contribute to maintaining healthy skin. By adopting a proactive approach to skincare and lifestyle choices, individuals can reduce their risk of developing these conditions and promote overall skin health.



