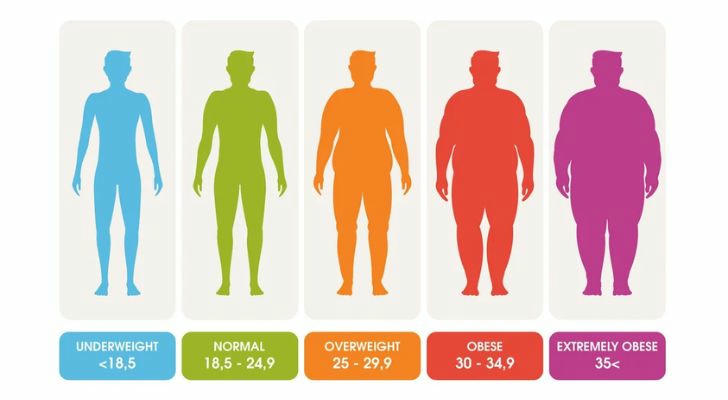
Obesity is a growing global health concern that affects millions of people across all age groups. Defined as having a body mass index (BMI) of 30 or higher, obesity is not just a cosmetic issue; it is a serious medical condition that can lead to various health complications. Understanding the causes, symptoms, and consequences of obesity, as well as exploring effective treatment options, is crucial for anyone looking to reclaim their health and well-being.

Why Ignoring obesity Isn’t an Option
Obesity is a critical global health issue that demands urgent attention. Yes, we must take it seriously. Ignoring obesity can lead to severe consequences, including:
-
Chronic Diseases: Obesity significantly increases the risk of type 2 diabetes, heart disease, hypertension, and certain cancers.
-
Mental Health Struggles: It is often linked to depression, anxiety, and low self-esteem due to societal stigma and body image issues.
-
Reduced Quality of Life: Obesity can limit mobility, disrupt sleep, and diminish energy levels, affecting daily activities and relationships.
-
Economic Burden: It strains healthcare systems and reduces productivity, impacting both personal finances and societal resources.
-
Shortened Lifespan: Severe obesity is associated with a higher risk of premature death.
-
Cardiovascular Diseases: Obesity increases the risk of heart disease, high blood pressure, and stroke due to the strain it places on the heart and blood vessels.
-
Joint Problems: The added weight puts extra stress on joints, leading to conditions such as osteoarthritis.
-
Respiratory Issues: Obesity can contribute to sleep apnea and other respiratory problems, affecting overall health and quality of life.
Causes of Obesity
Obesity is a complex condition influenced by a variety of factors, including:
-
Genetic Factors: Genetics can play a significant role in determining an individual's susceptibility to obesity. Certain genes may affect how the body processes food and stores fat.
-
Dietary Habits: The consumption of high-calorie, low-nutrient foods, such as fast food, sugary beverages, and processed snacks, contributes significantly to weight gain. Overeating and poor portion control are also common culprits.
-
Physical Inactivity: Sedentary lifestyles, characterized by prolonged periods of sitting and minimal physical activity, are a major contributor to obesity. Modern conveniences, such as cars and technology, have reduced the need for physical exertion.
-
Psychological Factors: Emotional factors, such as stress, anxiety, and depression, can lead to overeating or unhealthy eating habits. Some individuals may use food as a coping mechanism.
-
Environmental Influences: The environment in which a person lives can impact their eating and activity habits. Limited access to healthy foods, safe places to exercise, and education about nutrition can all contribute to obesity.
Symptoms of Obesity
The symptoms of obesity can vary, but common indicators include:
-
Excess body fat, particularly around the abdomen
-
Difficulty in performing physical activities
-
Fatigue and low energy levels
-
Joint pain, particularly in weight-bearing joints
-
Sleep apnea or other sleep disturbances
-
Increased sweating and body odor
-
Low self-esteem and body image issues
Treatment Options for Obesity
Fortunately, obesity is a treatable condition. Various approaches can help individuals achieve and maintain a healthy weight:
-
Dietary Changes: Adopting a balanced diet rich in fruits, vegetables, whole grains, and lean proteins is essential. Reducing the intake of processed foods, sugars, and unhealthy fats can lead to significant weight loss.
-
Physical Activity: Regular exercise is crucial for weight management. Aim for at least 150 minutes of moderate-intensity aerobic activity each week, along with strength training exercises.
-
Behavioral Therapy: Counseling and support groups can help individuals address emotional eating and develop healthier habits. Cognitive-behavioral therapy (CBT) is particularly effective in changing negative thought patterns related to food and body image.
-
Medications: In some cases, healthcare providers may prescribe weight-loss medications to assist with weight management. Common options include:
- Orlistat (Alli, Xenical)
This medication works by inhibiting fat absorption in the intestines.
- Phentermine-topiramate (Qsymia)
A combination of an appetite suppressant and an anticonvulsant that helps reduce hunger and increase feelings of fullness.
- Liraglutide (Saxenda)
Originally developed for diabetes, this medication helps control appetite and promote weight loss.
- Surgery
For individuals with severe obesity or those who have not had success with other treatments, bariatric surgery may be an option. Procedures such as gastric bypass or sleeve gastrectomy can lead to significant weight loss and improvements in health.

Personal Success Stories
Case 1: Emily's Transformation
Emily, a 32-year-old marketing professional, struggled with obesity for most of her adult life. At her heaviest, she weighed 110 kg (242 lbs) and had a BMI of 38. Emily's weight gain was primarily due to a sedentary lifestyle and poor eating habits, often relying on fast food for convenience.
Realizing that her weight was affecting her health and self-esteem, Emily decided to make a change. She began by consulting a nutritionist who helped her develop a personalized meal plan focused on whole foods and portion control. Emily also incorporated regular exercise into her routine, starting with daily walks and gradually increasing her activity level to include strength training and cardio workouts.
Over the course of a year, Emily lost 30 kg (66 lbs) and significantly improved her overall health. She reported feeling more energetic, confident, and happier. Emily now shares her journey on social media, inspiring others to take charge of their health and make positive lifestyle changes.
Case 2: David's Journey
David, a 45-year-old father of two, faced obesity after years of unhealthy eating and a lack of physical activity. Weighing 130 kg (286 lbs) at his peak, David experienced numerous health issues, including high blood pressure and sleep apnea. Concerned about his health and the impact on his family, he sought help from a healthcare professional.
David's treatment plan included a combination of dietary changes, increased physical activity, and medication. He was prescribed orlistat to assist with weight loss while he adopted a Mediterranean-style diet rich in fruits, vegetables, whole grains, and healthy fats. David also committed to exercising regularly, participating in group fitness classes, and engaging in family activities that promoted movement.
After two years of dedication and hard work, David lost 40 kg (88 lbs) and improved his health markers significantly. He no longer needed medication for high blood pressure and felt more active and engaged with his family. David now advocates for healthy living and encourages others to seek help and support in their weight loss journeys.

Frequently Asked Questions About Obesity
Q: What is the difference between overweight and obesity?
A: Overweight is defined as having a BMI between 25 and 29.9, while obesity is defined as having a BMI of 30 or higher. Both conditions increase the risk of health problems.
Q: Can obesity be inherited?
A: Yes, genetics can play a role in obesity. However, lifestyle choices and environmental factors also significantly influence weight.
Q: Is it possible to lose weight without exercise?
A: While dietary changes can lead to weight loss, incorporating physical activity is essential for long-term weight management and overall health.
Q: Are weight-loss medications safe?
A: Weight-loss medications can be effective for some individuals, but they may have side effects. It is important to discuss the risks and benefits with a healthcare provider.
Q: How can I support a friend or family member struggling with obesity?
A: Offer encouragement and support without judgment. Encourage healthy habits, participate in activities together, and be a listening ear when they need to talk about their challenges.
Conclusion
Obesity is a significant health issue that can have serious consequences, but it is not insurmountable. By understanding the causes, symptoms, and risks associated with obesity, individuals can take proactive steps toward a healthier lifestyle. Success stories like those of Emily and David demonstrate that with determination, support, and the right resources, it is possible to overcome obesity and reclaim one's health. If you or someone you know is struggling with obesity, remember that change is possible, and seeking help is the first step toward a brighter, healthier future.