When it comes to borrowing against the equity in your home, two popular options are a Home Equity Line of Credit (HELOC) and a home equity loan. While both allow you to tap into your home’s value, they function quite differently and serve different financial needs. Understanding these differences can help you make an informed decision about which option is best for you.

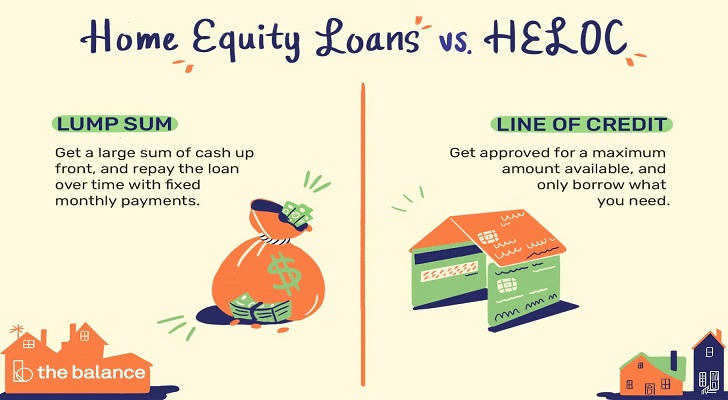
What is a Home Equity Loan?
A home equity loan is a type of second mortgage that allows you to borrow a lump sum of money based on the equity you have in your home. This loan is typically offered at a fixed interest rate, meaning your monthly payments will remain consistent throughout the life of the loan, which usually ranges from 5 to 30 years.
Key Features of Home Equity Loans:
- Lump Sum Payment: You receive the entire loan amount upfront, which is ideal for large, one-time expenses such as home renovations, debt consolidation, or major purchases.
- Fixed Interest Rate: Your interest rate is locked in for the duration of the loan, providing predictable monthly payments.
- Repayment Terms: You start repaying the loan immediately, which includes both principal and interest.

What is a HELOC?
A Home Equity Line of Credit (HELOC) is a revolving line of credit that allows you to borrow against your home’s equity as needed. It functions similarly to a credit card, where you can withdraw funds up to a certain limit during a specified draw period, typically lasting 5 to 10 years.
Key Features of HELOCs:
- Flexible Borrowing: You can borrow as much or as little as you need, up to your credit limit, making it suitable for ongoing expenses like home improvements or education costs.
- Variable Interest Rate: Most HELOCs have variable interest rates, which means your payments can fluctuate based on market conditions.
- Draw and Repayment Periods: During the draw period, you may only be required to pay interest on the amount borrowed. After this period, you enter the repayment phase, where you pay back both principal and interest.
Comparing HELOCs and Home Equity Loans
1. Purpose of Borrowing
- Home Equity Loan: Best for one-time, large expenses.
- HELOC: Ideal for ongoing expenses or projects where costs may vary.
2. Interest Rates
- Home Equity Loan: Generally offers fixed rates.
- HELOC: Typically has variable rates, which can change over time.
3. Payment Structure
- Home Equity Loan: Fixed monthly payments that include both principal and interest.
- HELOC: Payments may vary, especially during the draw period when you might only pay interest.
4. Access to Funds
- Home Equity Loan: You receive a lump sum at the beginning.
- HELOC: You can withdraw funds as needed, up to your credit limit.
5. Risk Factors
- Both options use your home as collateral, meaning failure to repay could result in foreclosure. However, the variable rates of a HELOC can introduce additional risk if interest rates rise significantly.
How to Calculate Home Equity
Home equity is the portion of your home that you truly own, which can be a valuable asset when considering loans or selling your property. Calculating your home equity is relatively straightforward. Here’s how to do it:
Step-by-Step Guide to Calculate Home Equity
1. Determine Your Home's Current Market Value
The first step in calculating your home equity is to find out how much your home is currently worth. You can do this by:
- Getting a Professional Appraisal: Hire a licensed appraiser to assess your home’s value.
- Comparative Market Analysis (CMA): Consult a real estate agent for a CMA, which compares your home to similar properties in your area.
- Online Valuation Tools: Use online real estate platforms that provide estimated home values based on recent sales data.
2. Find Out Your Outstanding Mortgage Balance
Next, you need to know how much you still owe on your mortgage. This information can typically be found on your most recent mortgage statement or by contacting your lender.
3. Use the Home Equity Formula
Once you have both figures, you can calculate your home equity using the following formula: Home Equity = Current Market Value of Home - Outstanding Mortgage Balance
4. Example Calculation
Let’s say your home is currently valued at $300,000, and you have an outstanding mortgage balance of $200,000.
Using the formula: Home Equity = $300,000 - $200,000 Home Equity = $100,000 , In this example, your home equity would be $100,000.
Additional Considerations
- Home Improvements: Keep in mind that significant renovations or improvements can increase your home’s market value, thereby increasing your equity.
- Market Fluctuations: The real estate market can fluctuate, affecting your home’s value and, consequently, your equity.
- Equity Percentage: You can also express your home equity as a percentage of your home’s value:

Which Option is Right for You?
Choosing between a HELOC and a home equity loan depends on your financial situation and goals. If you need a large sum for a specific purpose and prefer predictable payments, a home equity loan may be the better choice. On the other hand, if you anticipate needing funds over time for various expenses, a HELOC offers flexibility and convenience.
Before making a decision, consider consulting with a financial advisor to evaluate your options and ensure you choose the best product for your needs. Both HELOCs and home equity loans can be valuable tools for leveraging your home’s equity, but understanding their differences is crucial for making an informed choice.
In conclusion, whether you opt for a HELOC or a home equity loan, both can provide financial relief and help you achieve your goals. Just be sure to weigh the pros and cons carefully and choose the option that aligns best with your financial strategy.



